
You can download Disk2Vhd here (879 KB) Step 2 - Unzip and Executeĭisk2vhd can run on a system that’s online, that’s possible because it uses Windows' Volume Snapshot capability to create consistent point-in-time snapshots of the volumes you want to include in a virtualization. Disk2vhd runs on Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and higher, including 圆4 systems. We’re going to be using Disk2vhd for this guide, and it only supports Microsoft operating systems. Although, you can use Disk2Vhd virtual disks.
Oracle VirtualBox - This open source VM program, unfortunately, doesn’t provide any user interface tool and the process is pretty much manual but supports both Windows and Linux. Parallels - Even though it offers VM programs for Windows, Linux and Mac operating systems, it only provides a tool (known as Parallels Transporter Agent) for Windows and Linux. Microsoft Sysinsternals provides Disk2vhd which converts a physical system into a VHD. Microsoft Hyper-V - Only supports Windows virtualization. 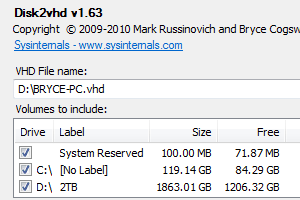
It’s able to convert local and remote physical machines without any downtime.
VMware - Supports virtualization of both Windows and Linux with a tool called vCenter Converter. Most common virtual machine programs offer some kind of virtualization tool, also called a physical-to-virtual tool (P2V): You can boot a virtual disk on “hosted” virtual machine programs, or even directly on server’s hardware using “bare metal” hypervisors. The process will basically create a complete copy of your physical machine’s OS to be used by a host. 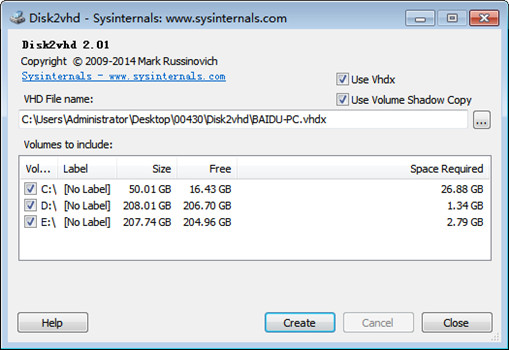
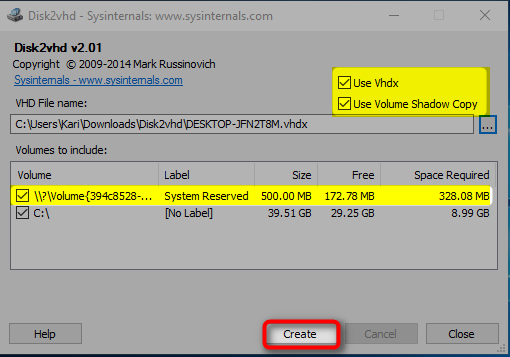
Virtualization of a physical machine is the process that converts a physical operating system (OS) partition into a virtual hard drive (VHD).







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
